Pre-Implementation Genetic Screening
Genetic Testing
- Preconception
- Preimplantation
- Prenatal
- New Born Sceening
Need for PGD Screening
- Older women likely to produce abnormal Oocytes
- Leads to chromosomally abnormal embryos
- Increase in miscarriage
- Lower pregnancy rate
- Chromosomes commonly involved
Prenatal Diagnosis
- Chorionic villus sampling (CVS) 10-14wks
- Amniocentesis (15-16wks)
- Fetal blood sampling (FBS)
Preimplantation Genetic Screening - Diagnosis
Implantation genetic diagnosis is an emerging technique that detects genetic and chromosomal abnormalities in IVF embryos before embryo transfer.
- Early Embryos
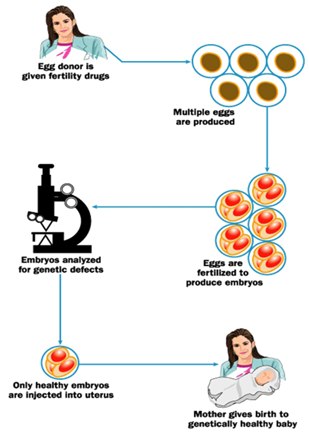
- IVF for selection of healthy embryo for transfer to the uterus
PGD and PGS recommended
- In case of multiple first trimester miscarriages
- When the candidate mother is over 36 years
- Where there is a history of multiple IVF failures
- When the couple demonstrate chromosomal abnormalities
- When there is already one child with a genetic syndrome, which can be diagnosed in laboratory
- When there is family history of cerebral damage or abnormal development.
- Decreasing chance of chromosome abnormality in ongoing pregnancy
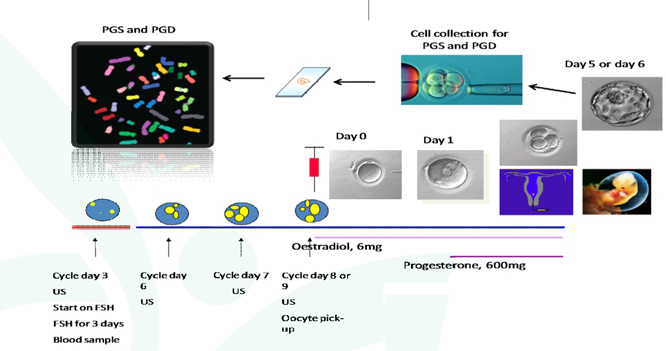
FISH Diagnosis
- Analyse chromosomes
- Sexing for X-linked disease
- Chromosome abnormalities
- Age related aneuoploidy

To whom it beneficial
- Couples one or both having genetic disorder
- Couples whom have familial history on genetic disorders
PGD disease like
Alzheimer's, Anemia, Cystic fibrosis, Thalassemia, Huntington's Disease, Hemophilia, Polycystic kidney disease etc.
- Pre-implantation genetic screening is reliable, for successful embryo implantation
- Seeing is not believing. Morphology is insufficient
- PGS is a kind of chromosome “painting” (or FISH) using fluorescent probes specific for each chromosome. These allow number and size of each chromosome to be checked.
- Useful for identifying aneuploidies (incorrect chromosome numbers) and translocations
PGS (Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis/Screening)
PGS screens the embryo to ensure that the correct number (46) of chromosomes present. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes - for a total of 46. Abnormality in chromosome number leads to Aneuploidy.
Genetic analysis of a single cell from trophectoderm biopsy of blastocyst stage of day 5 or 6 , about 5 cells are snipped off for PGS testing. At this stage there are many more cells present in the embryo. This allows multiple cells to be removed from the trophectoderm (precursors to the placenta). The inner mass cells (precursors to the fetus) can be left undisturbed during the biopsy.
PGS test is done in conjunction with in vitro fertilization (IVF) to improve the chances of a “normal” pregnancy.
PGD Screening
PGD is helpful in predicting single gene defects by screening embryos for a particular genetic disorder and to prevent transmission of genetic disease
- When, one or both partners in a couple are carriers of the genetic mutation that could leave and lead to a serious medical condition in the child. In-vitro fertilization and pre-implantation genetic diagnosis PGD testing can be performed on their embryos.
- Can be performed with amniocentesis at about 16 to 18 weeks of pregnancy or with chorionic villus sampling at about 11 to 12 weeks. If any abnormalities found, the patients can choose to terminate the baby.
- PGD can also be done with IVF trophectoderm biopsy done before uterus implantation.